EGD
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy, commonly known as EGD or upper endoscopy, is a medical procedure that allows a doctor to examine the lining of the upper part of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract, which includes the esophagus, stomach, and the beginning of the small intestine (duodenum). This procedure is performed using an endoscope, a flexible tube with a light and camera at the end, which transmits images to a monitor, providing a detailed view of the upper GI tract.
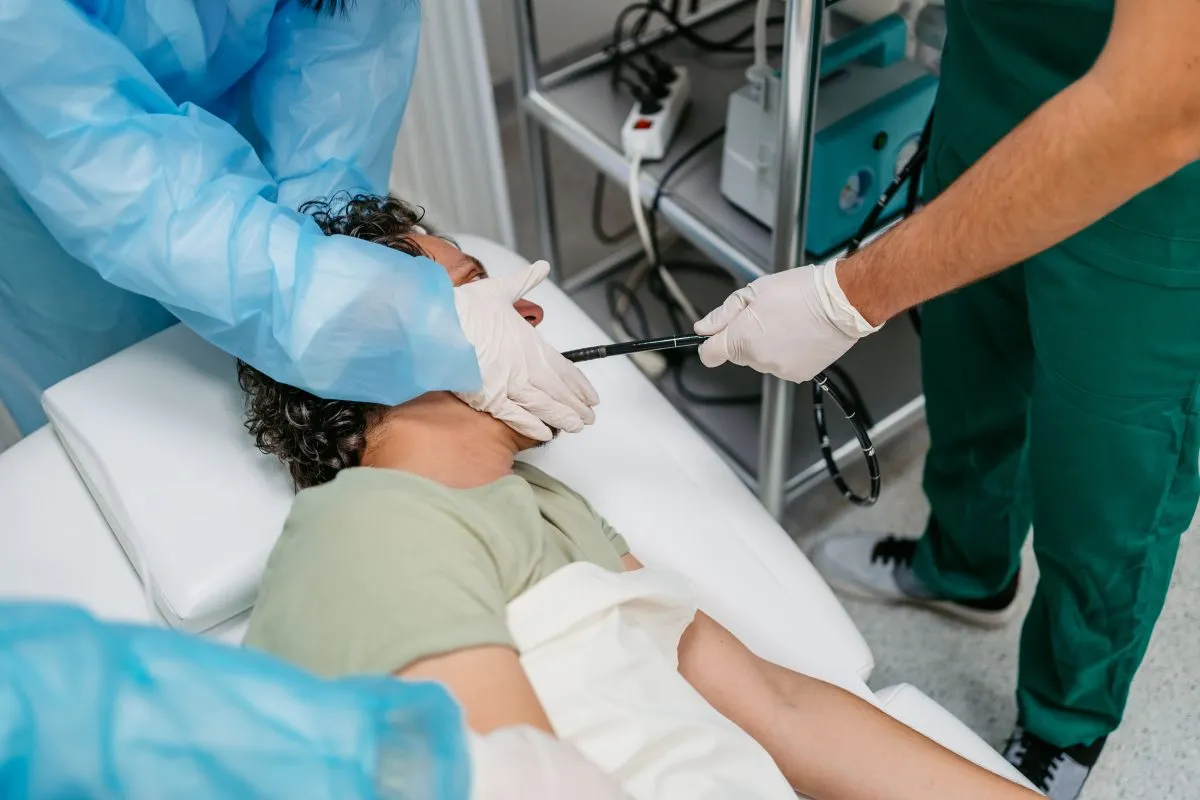
Investigating Symptoms: To diagnose the cause of symptoms such as persistent heartburn, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia), upper abdominal pain, nausea, vomiting, or unexplained weight loss.
Detecting Conditions: To identify conditions such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcers, celiac disease, esophageal strictures, Barrett's esophagus, and cancers of the upper GI tract.
Treating Conditions: EGD can also be used therapeutically to treat certain conditions, such as removing polyps, dilating strictures, controlling bleeding, or removing foreign objects
